User:Becha/InternetPlumbing: Difference between revisions
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
** Home router is (usually) a gateway, firewall, and NAT box at the same time | ** Home router is (usually) a gateway, firewall, and NAT box at the same time | ||
[[File:Tcpip pat.gif| | [[File:Tcpip pat.gif|400px]] [[File:Nat-images.png]] | ||
* Advanced: double-NAT aka NAT444 | * Advanced: double-NAT aka NAT444 | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 6 April 2016

Lectures at Hacking Feminism
Fist lecture in this series:
- 6 April 2016, 8PM
- At LAG
- By Becha
- https://wiki.laglab.org/Hacking_Feminism
GOALS:
- Empower each-other with knowledge
- Learn the basics technical concepts of underlying Internet works
- Discover & emphesise roles of women
- Practice & get our hands dirty
- Work on the alternatives together!
- Personal goals: learn by teaching; develop series of lectures; practice practice practice!
- What's your goals?
Internet Plumbing
Internet Plumbing is a word-game with multiple layers of meaning (ha! a recursive pun ;-)

Series of Tubes
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Series_of_tubes
- Andrew Blum 2012 book " Tubes: A Journey to The Center of The Internet" , starts with the squirrel that ruins his Internet (connection/tube).
- http://knowyourmeme.com/memes/series-of-tubes
- http://www.submarinecablemap.com/
Ubiquitous and complicated as plumbing?
- Internet as a utility
- just like "plumbing" (water & sewage), there is underlying "technology" to it, so complex, that no-one seems to grasp how all of it works
- 60% of the population of the planet does NOT have "teh Internets", and 30% does not have plumbing either (http://www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/sanitation.shtml)

Women's role
- Women in history of computing, engineering, internet: Ladies_Night/women_in_history_of_STEM
- Women who wrote about Internet: history, hacking, ethics, (hack)tivism, governance, economy, (anti)capitalism Female_experts
- Ladies_Night#Gender_gap_in_tech
- Ladies_Night#Increasing_the_gender_diversity
- Ladies_Night#Anti-capitalism
- Geek/cyber feminism: Ladies_Night#Feminism
Participate, take action, join
- contribute to this wiki page
- learn more!
- join mailing lists discussions for technical policy development & Internet governance
- learn to code & take part in FLOSS community
- join a hackerspace
- teach your skills to others
- contact me: BECHA @ xs4all dot nl // @Ms_Multicolor
Basics
Internet is network of networks
Step by step
- "Small network" -- computers "talking" to each other
- Local Area Network = LAN
- With cables (ethernet), or Wireless (WiFi)
- How do they find each other? using unique numbers: MAC (ethernet) address (layer 2), translated by ARP (MAC to IP address)
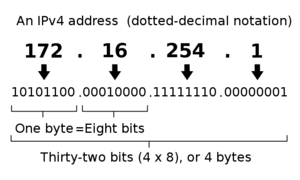
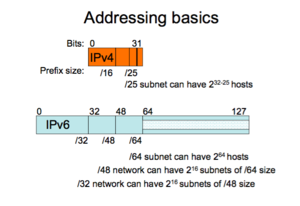
- About IP (Internet Protocol) addresses
- binary numbers, written as decimal (IPv4) or hexadecimal (IPv6)
- Can be "public" or "private" (=local)
- What is the format?
Exercise!!
- Typical / mainstream home (or small office) network
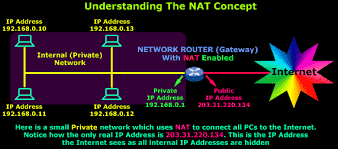
- Private IP addresses
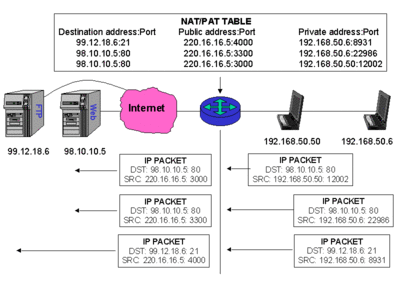
- NAT = Network Address Translation - translated from multiple private to (usually) one public IP address
- Home router is (usually) a gateway, firewall, and NAT box at the same time
- Advanced: double-NAT aka NAT444
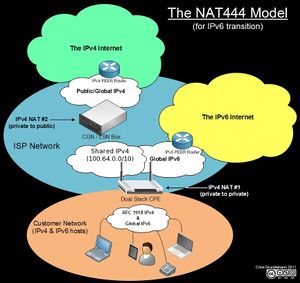
- Further reading about IPv6: User:Becha/DeeperIPv6
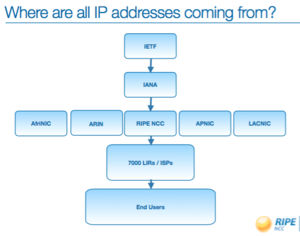
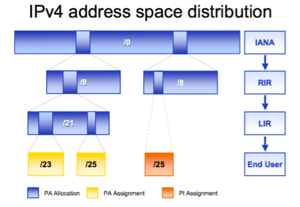
- Where do the IP addresses come from?
- Hierarchical distribution (see charts)
- Principles: fairness, aggregation, conservation, registration
- Used to be "needs based", not open to "market forces"
- Policies for distribution ("rules") are developed in open, transparent, bottom-up process
- IPv4 is "legacy", has run out - but is still DE FACTO THE ONLY STANDARD in use!
- Connecting "to the Internet"
- usually through commercial ISP (Internet Service Provider): dial-up, fibre, ...
- "free Wifi"
- over mobile!
- alternatively: community-mesh-peer-to-peer
- ISPs connecting with each other
- ISPs are "autonomous networks" (autonomous from each other)
- Using BGP and AS numbers https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Border_Gateway_Protocol
Exercise!! & Video!!!
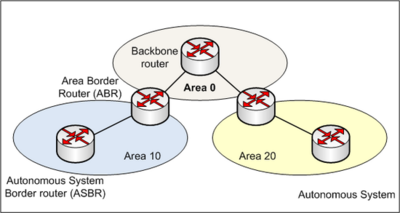
- Relationships between "providers"
- direct peering: between more-less same size & same "importance" ISPs
- usually at IXP (Internet eXchange Point, e.g. Ams-IX, LINX...)
- "buying transit" from a "national Telco", usually
- large providers and carriers create a "backbone"
- Further reading: Social scientist explains: Uta Meier-Hahn
- Internet Interconnection: Networking in Uncertain Terrain https://labs.ripe.net/Members/uta_meier_hahn/internet-interconnection-networking-in-uncertain-terrain
- The Regulatory Conditions of IP Interconnection 2016 https://labs.ripe.net/Members/uta_meier_hahn/the-regulatory-conditions-of-ip-interconnection
Video!!! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QuBde4Sn3f0
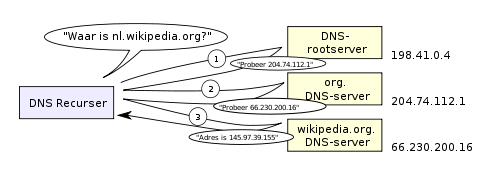
- How do humans find services on the Internet? -> BY NAME!
- numbers (IP addresses) are translated to names by DNS
- web-sites, servers, services have DNS "names"
- hierarchical distribution of names
- Advanced concepts: resolver, cashing, primary & secondary name-servers, master-slave, recursive resolver, labels, zones
- DNS with NAT
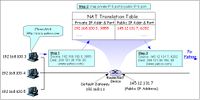
Exercise!!
Exercises
User:Becha/InternetPlumbing/Exercises
Videos
- youtube hijack
- How IXP's work
- Net of Rights
Want to learn more?
- ISOC on-line course: https://www.internetsociety.org/what-we-do/inforum-learn-online/inforum-course-introduction-network-operations
- RIPE NCC training materials are free to use: https://ripe.net/training
- See also "resources"
Networking Principles
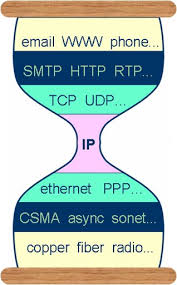
Concepts

- packets & packet switching
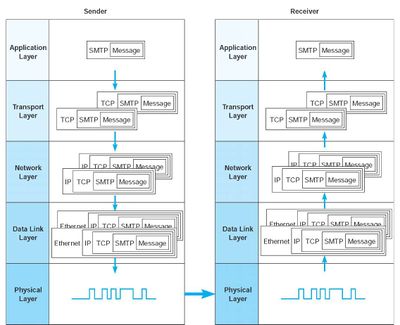
- encapsulation
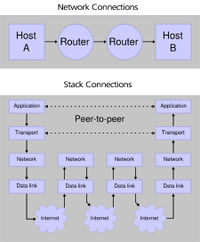
- layered network model
- (open) protocols & (open) standards
- end-to-end principle
- ports
- server/client architecture
- cryptography
Comparing OSI & TCP / IP layers
Original borrowed from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_model
| TCP / IP Model | OSI Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | OSI Layer | Protocol data unit (PDU) | Function | Examples |
| Application | 7. Application | Data | High-level APIs, including resource sharing, remote file access, directory services and virtual terminals | TLS, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, SSH, Telnet, BGP! |
| 6. Presentation | Translation of data between a networking service and an application; including character encoding, data compression and encryption/decryption | CSS, GIF, HTML, XML, JSON | ||
| Transport | 5. Session | Managing communication sessions, i.e. continuous exchange of information in the form of multiple back-and-forth transmissions between two nodes | RPC, SCP, NFS, PAP, | |
| 4. Transport | Segment (TCP) / Datagram (UDP) | Reliable transmission of data segments between points on a network, including segmentation, acknowledgement and multiplexing | NBF, TCP, UDP | |
| Network / Internet |
3. Network | Packet | Structuring and managing a multi-node network, including addressing, routing and traffic control | AppleTalk, ICMP, IPsec, IPv4, IPv6 |
| Link layer |
2. Data link | Frame | Reliable transmission of data frames between two nodes connected by a physical layer | IEEE 802.2, L2TP, LLDP, MAC, PPP, ATM, MPLS |
| 1. Physical | Bit | Transmission and reception of raw bit streams over a physical medium | DOCSIS, DSL, Ethernet physical layer, ISDN, USB | |
Cross-layer functions:
- ARP is used to translate IPv4 addresses (OSI layer 3) into Ethernet MAC addresses (OSI layer 2).
- Domain Name Service is an Application Layer service which is used to look up the IP address of a given domain name. Once a reply is received from the DNS server, it is then possible to form a Layer 3 connection to the third-party host.
- etc
Resources
Many many more resources: books, videos:
Links:
- http://en.flossmanuals.net/bypassing-censorship/ch006_chapter-1-how/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_protocol_suite
- http://what-when-how.com/data-communications-and-networking/network-and-transport-layers-data-communications-and-networking/
- http://what-when-how.com/data-communications-and-networking/network-models-data-communications-and-networking/
- http://www.laneye.com/network/how-network-works/mac-address-and-ip-address-relationship.htm
- https://www.amplicon.com/building/networking-principles.cfm#ip
- DNS & CDNs: Internet plumbing: Think globally, route locally, Mar 16th 2011, http://www.economist.com/node/21016766/print
Acronyms!
- TCP/IP
- IPv4, IPv6: Internet Protocol (IP) addresses
- NAT: Network Address Translation
- DNS: Domain Name System
- ASN: Autonomous System Number
- used for BGP routing (Border Gateway Protocol)
- IXP: Internet eXchange Point
- SMTP
- HTTP
- CDN
Advanced topics
Layers as an allegory

Left: OSI Model T-shirt enhanced to include an 8th and 9th layer as defined by Evi Nemeth: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evi_Nemeth // https://www.isc.org/product/isc-9-layer-osi-model-cotton-t-shirt/
(TODO: add ISC reference to Evi's wikipedia page!!)
Right: back of the T-shirt from the IETF75 in Stockholm, 2005
ABSTRACTION
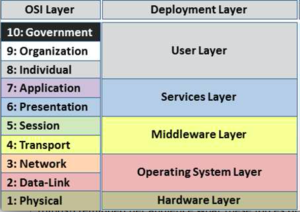
Explaining complex concepts using layers is a useful abstraction.
Goal here is to illustrate layers by practical examples, and point out owners, developers, dangers, mitigations & alternatives.
This is not exactly technically correct, for the detail oriented people!
| Number | Layer name | Example | Practically | Owner | Developed by | Vulnerabilities / Dangers | Mitigation / Securing | Alternatives | |
| 9 | Organisation / Political | (Internet) Governance | technical community, civil society, governments | IGF (Internet Governance Forum), UN, ITU, IETF, ICANN, | awareness, take part! | someone will build a new *net, AlterNet :-) | |||
| 8 | Individual / Financial | Operating System (OS) + choice of software | Linux, FreeBSD, Minix...; iOS, Android, Windows... | User! | programmers & developers: FLOSS community; Apple, Google,Micro$oft |
backdoors, surveillance, spying on users; lock-in; monopoly; | community participation; unionization of programmers; see articles here [yy] | knowledge, self-empowerment, solidarity | |
| 7 | Application | 7.3 -> VoIP | skype | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.2 -> SMTP | |||||||||
| 7.1 HTTP: web, WWW | web sites! LoLCats! | individuals, on their own servers! blogs (blogspot?), mainstream media, hosting companies; CDNs (Akamai, Amazon...); corporations: Google, Facebook, Twitter... YouTube.. |
W3c, IETF | censorship; silos; walled gardens; commercialization, consumerism; | technically: httpS, SSL, TLS; Tor; politically: activism, digital human rights; associations of users; |
torrent! p2p! alternative social media! | |||
| 6 | Presentation | HTML, CSS, JSON | |||||||
| 5 | Session | BGP (actually layer 7...) | routing: exchanging AS reachability info via gossip: based on trust & peering agreements! physical routers by routers: Cisco/Juniper (commercial monopolists ;-) |
Large ISPs; Tier1 / Tier2 ; IXPs!! RIRs give out AS numbers | "routing-wg" @ RIPE; *NOGs! (nano, nlnog, grnog; peering forums; Euro-IX); IETF; Open-Source community ; hackers | "route hijacks", government regulation & takeover (killer switch), hierarchies; | technically: BGPsec, IRR, RPKI; politically: influencing governance |
p2p protocols, Betman [xx]; MPLS, SDN; Tor?! | |
| 4 | Transport | UDP -> e.g. DNS (see above!) | www.belastingdiest.nl | User; Registrar, Registry, ccTLD, gTLD, ICANN, US government! | DNS OARC, IETF, root-nameserver operators, ICANN, IGF/UN/ITU | "balkanisation", US hegemony; internationalization; censorship; | technically: DNSSEC, DANE ; Tor; politically: participating in governance |
Alternative trees; blockchain (namecoin); etc | |
| 3 | Network | Internet / IP | ifconfig; IPv4, NAT, 10.10.10.10, IPv6 | no-one: IP addresses are "leased"! (PI,PA,LIR,RIR,IANA,IETF) |
RIR PDP, IANA, IETF | hierarchy, run-out, incompatibility, market forces; surveillance | IPSec | Blockchain? GSM? Radio? | |
| 2 | Data-link | MAC addresses, Ethernet device drivers, WiFi drivers | licensed to users | Broadcom, Realtech, INTEL.. | patents, closed source, Intellectual Property Laws | open source SW, open HW | ?! | ||
| 1 | Physical | Network connections | Ethernet cables, WiFi antennas, fibers, satellites, satellite dishes, base-stations, under-sea cables ; POTS (old-fashioned phones -> BBS, dialup) | Individuals communities, ISP, "carriers", corporations, governments, |
Hackers commercial companies, governments |
"ownership" models; hierarchy of server-client model; pollution & distraction of Earth; surveillance | commoning; shared infrastructure; development of sustainable technologies (?!), recycling; awareness & activism | Community WiFi, Project Loon, Drones | |
| HW - end user equipment | Computer, tablet, phone... | User | Commercial companies: Apple, Siemens, Samsung... | Un-ethical manufacturing, security backdoors, pollution caused by e-waste disposal, | Hard: | Open HW movement; fair-phone; DIY, Repair Cafes, fair-trade... |
Security, Privacy, Avoiding Censorship
- IPSec
- DNSSEC
- BGP security & plumbing:
- User Self-help:
Alternatives
MeshNet: "Hackers and philosophers building an utopia together": http://becha.home.xs4all.nl/hackers-philosophers-utopian-network-dec-2012-becha.pdf

November 2014: Nature will have the last word, on Future of Technology, RIPE69 https://wiki.techinc.nl/index.php/File:Nature-speaking-on-future_of_the_internet-RIPE69.pdf
UnCivilization: critical thinking about Internet & capitalism: https://lists.puscii.nl/wws/info/uncivilization
Playfull: Internet Simulator: https://github.com/nsec/the-internet
- Alternative Network Deployments: Taxonomy, characterization, technologies and architectures
https://www.ietf.org/id/draft-irtf-gaia-alternative-network-deployments-04.txt
- The Critical Engineering Manifesto: https://www.criticalengineering.org/
Next topics
Internet Governance
See this lecture : Internet_Governance_Digital_Culture#Internet_Governance
Internet_Governance_and_hackers
Traceroute Much?
User:Becha/InternetPlumbing/Traceroute_Much