Difference between revisions of "User:Becha/InternetPlumbing"
(→Internet Plumbing) |
(→Overview) |
||
| Line 131: | Line 131: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Description of OSI layers== | ||
| + | The recommendation X.200 describes seven layers, labeled 1 to 7. Layer 1 is the lowest layer in this model. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! colspan="5" | OSI Model | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! colspan="2" | Layer | ||
| + | ! [[Protocol data unit]] (PDU) | ||
| + | ! style="width:30em;" | Function<ref>{{Cite web | title = The OSI Model's Seven Layers Defined and Functions Explained | work = Microsoft Support | accessdate = 2014-12-28 | url = https://support.microsoft.com/kb/103884}}</ref> | ||
| + | ! Examples | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! rowspan="4" | Host<br />layers | ||
| + | | style="background:#d8ec9b;" | 7. [[Application layer|Application]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#d8ec9c;" rowspan="3" | [[Data (computing)|Data]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#d8ec9c;" | <small>High-level [[API]]s, including resource sharing, remote file access, [[directory service]]s and [[virtual terminal]]s</small> | ||
| + | | [[Transport Layer Security|TLS]], [[FTP]], [[HTTP]], [[HTTPS]], [[SMTP]], [[Secure Shell|SSH]], [[Telnet]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="background:#d8ec9b;" | 6. [[Presentation layer|Presentation]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#d8ec9b;" | <small>Translation of data between a networking service and an application; including [[character encoding]], [[data compression]] and [[Encryption|encryption/decryption]]</small> | ||
| + | | [[CSS]], [[GIF]], [[HTML]], [[XML]], [[JSON]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="background:#d8ec9b;" | 5. [[Session layer|Session]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#d8ec9b;" | <small>Managing communication [[Session (computer science)|sessions]], i.e. continuous exchange of information in the form of multiple back-and-forth transmissions between two nodes</small> | ||
| + | | [[Remote Procedure Call|RPC]], [[DECnet|SCP]], [[Network File System|NFS]], [[Password authentication protocol|PAP]], | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="background:#e7ed9c;" | 4. [[Transport layer|Transport]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#e7ed9c;" | [[Packet segmentation|Segment]] (TCP) / [[Datagram]] (UDP) | ||
| + | | style="background:#e7ed9c;" | <small>Reliable transmission of data segments between points on a network, including [[Packet segmentation|segmentation]], [[Acknowledgement (data networks)|acknowledgement]] and [[multiplexing]]</small> | ||
| + | | [[NetBIOS Frames protocol|NBF]], [[Transmission Control Protocol|TCP]], [[User Datagram Protocol|UDP]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! rowspan="3" | Media<br />layers | ||
| + | | style="background:#eddc9c;" | 3. [[Network layer|Network]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#eddc9c;" | [[Network packet|Packet]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#eddc9c;" | <small>Structuring and managing a multi-node network, including [[Address space|addressing]], [[routing]] and [[Network traffic control|traffic control]]</small> | ||
| + | | [[AppleTalk]], [[Internet Control Message Protocol|ICMP]], [[IPsec]], [[IPv4]], [[IPv6]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="background:#e9c189;" | 2. [[Data link layer|Data link]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#e9c189;" | [[Frame (networking)|Frame]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#e9c189;" | <small>Reliable transmission of data frames between two nodes connected by a physical layer</small> | ||
| + | | [[IEEE 802.2]], [[L2TP]], [[LLDP]], [[Media access control|MAC]], [[Point-to-Point Protocol|PPP]], [[Asynchronous Transfer Mode|ATM]], [[Multiprotocol Label Switching|MPLS]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="background:#e9988a;" | 1. [[Physical layer|Physical]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#e9988a;" | [[Bit]] | ||
| + | | style="background:#e9988a;" | <small>Transmission and reception of raw bit streams over a physical medium</small> | ||
| + | | [[DOCSIS]], [[DSL]], [[Ethernet physical layer]], [[ISDN]], [[USB]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <!----- {{Clear}} -------> | ||
| + | |||
==Participate, take action, join== | ==Participate, take action, join== | ||
Revision as of 08:38, 3 April 2016
Lecture at Hacking Feminism
- 6 April 2016, 8PM
- By Becha
- https://wiki.laglab.org/Hacking_Feminism
Internet Plumbing
Internet Plumbing is a word-game with multiple layers of meaning (ha! a recursive pun ;-)
Series of Tubes
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Series_of_tubes
- http://www.salon.com/2012/05/28/tubes_what_the_internet_is_made_of/
- http://knowyourmeme.com/memes/series-of-tubes
- http://www.submarinecablemap.com/
Ubiquitous and complicated as plumbing?
- Internet as a utility
- just like "plumbing" (water & sewage), there is underlying "technology" to it, so complex, that no-one seems to grasp how all of it works
- 60% of the population of the planet does NOT have "teh Internets", and 30% does not have plumbing either (http://www.un.org/waterforlifedecade/sanitation.shtml)
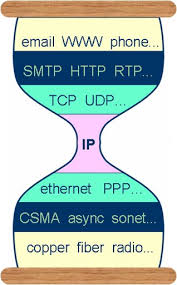
Acronyms!
- TCP/IP
- IPv4, IPv6: Internet Protocol (IP) addresses
- NAT: Network Address Translation
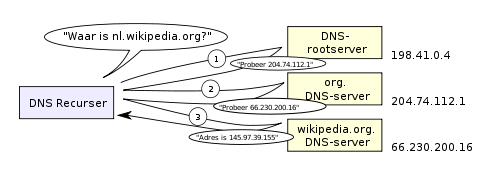
- DNS: Domain Name System
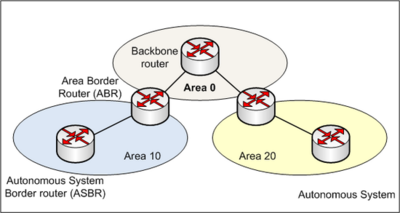
- ASN: Autonomous System Number
- used for BGP routing (Border Gateway Protocol)
- IXP: Internet eXchange Point
- SMTP
- HTTP
- CDN
Basics
Many many more resources: books, videos:
Links:
- http://en.flossmanuals.net/bypassing-censorship/ch006_chapter-1-how/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Internet_protocol_suite
- http://what-when-how.com/data-communications-and-networking/network-and-transport-layers-data-communications-and-networking/
- http://what-when-how.com/data-communications-and-networking/network-models-data-communications-and-networking/
- http://www.laneye.com/network/how-network-works/mac-address-and-ip-address-relationship.htm
- https://www.amplicon.com/building/networking-principles.cfm#ip
- DNS & CDNs: Internet plumbing: Think globally, route locally, Mar 16th 2011, http://www.economist.com/node/21016766/print
Security, Privacy, Avoiding Censorship
- IPSec
- DNSSEC
- BGP security & plumbing:
- User Self-help:
Alternatives
MeshNet: "Hackers and philosophers building an utopia together": http://becha.home.xs4all.nl/hackers-philosophers-utopian-network-dec-2012-becha.pdf
November 2014: Nature will have the last word, on Future of Technology, RIPE69 https://wiki.techinc.nl/index.php/File:Nature-speaking-on-future_of_the_internet-RIPE69.pdf
UnCivilization: critical thinking about Internet & capitalism: https://lists.puscii.nl/wws/info/uncivilization
Playfull: Internet Simulator: https://github.com/nsec/the-internet
Overview
| Layer | Example | Practically | Owner | Developed by | Vulnerabilities/Dangers | Securing | Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | HW - end user equipment | Computer, tablet, phone... | User | Commercial companies: Apple, Siemens, Samsung... | Un-ethical manufacturing, security backdoors, pollution caused by e-waste disposal, | Hard: | Open HW movement; fair-phone; DIY, Repair Cafes, fair-trade... |
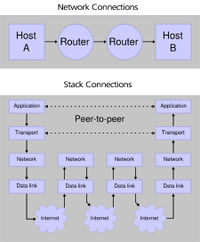
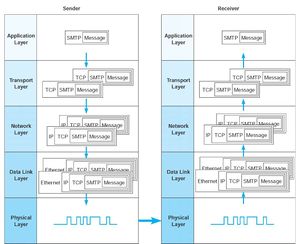
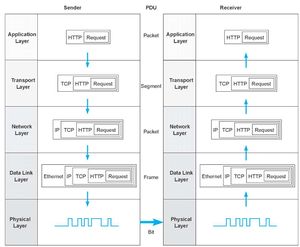
Description of OSI layers
The recommendation X.200 describes seven layers, labeled 1 to 7. Layer 1 is the lowest layer in this model.
| OSI Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | Protocol data unit (PDU) | Function<ref>Template:Cite web</ref> | Examples | |
| Host layers |
7. Application | Data | High-level APIs, including resource sharing, remote file access, directory services and virtual terminals | TLS, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, SSH, Telnet |
| 6. Presentation | Translation of data between a networking service and an application; including character encoding, data compression and encryption/decryption | CSS, GIF, HTML, XML, JSON | ||
| 5. Session | Managing communication sessions, i.e. continuous exchange of information in the form of multiple back-and-forth transmissions between two nodes | RPC, SCP, NFS, PAP, | ||
| 4. Transport | Segment (TCP) / Datagram (UDP) | Reliable transmission of data segments between points on a network, including segmentation, acknowledgement and multiplexing | NBF, TCP, UDP | |
| Media layers |
3. Network | Packet | Structuring and managing a multi-node network, including addressing, routing and traffic control | AppleTalk, ICMP, IPsec, IPv4, IPv6 |
| 2. Data link | Frame | Reliable transmission of data frames between two nodes connected by a physical layer | IEEE 802.2, L2TP, LLDP, MAC, PPP, ATM, MPLS | |
| 1. Physical | Bit | Transmission and reception of raw bit streams over a physical medium | DOCSIS, DSL, Ethernet physical layer, ISDN, USB | |
Participate, take action, join
Next: Internet Governance
See this lecture : Internet_Governance_Digital_Culture#Internet_Governance
Internet_Governance_and_hackers