Difference between revisions of "User:Becha/InternetPlumbing/Layers"
(→Comparing OSI & TCP / IP layers) |
(→Comparing OSI & TCP / IP layers) |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
* Domain Name Service is an Application Layer service which is used to look up the IP address of a given domain name. Once a reply is received from the DNS server, it is then possible to form a Layer 3 connection to the third-party host. | * Domain Name Service is an Application Layer service which is used to look up the IP address of a given domain name. Once a reply is received from the DNS server, it is then possible to form a Layer 3 connection to the third-party host. | ||
* etc | * etc | ||
| + | |||
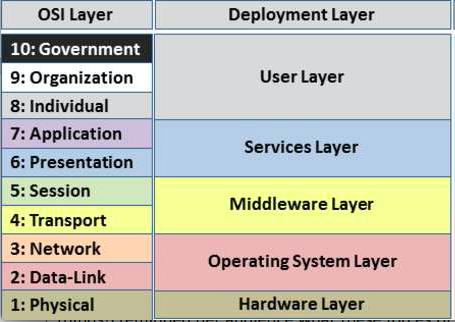
[[File:Osi-deployment-layers.png]] | [[File:Osi-deployment-layers.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Owners, Developers, Dangers, Mitigations, Alternatives== | ||
{| class="wikitable sortable" | {| class="wikitable sortable" | ||
| Line 67: | Line 70: | ||
!Developed by | !Developed by | ||
|Vulnerabilities/Dangers | |Vulnerabilities/Dangers | ||
| − | + | | Securing | |
| Alternatives | | Alternatives | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 09:56, 3 April 2016
Comparing OSI & TCP / IP layers
Original borrowed from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OSI_model
| TCP / IP Model | OSI Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Layer | OSI Layer | Protocol data unit (PDU) | Function | Examples |
| Application | 7. Application | Data | High-level APIs, including resource sharing, remote file access, directory services and virtual terminals | TLS, FTP, HTTP, HTTPS, SMTP, SSH, Telnet, BGP! |
| 6. Presentation | Translation of data between a networking service and an application; including character encoding, data compression and encryption/decryption | CSS, GIF, HTML, XML, JSON | ||
| Transport | 5. Session | Managing communication sessions, i.e. continuous exchange of information in the form of multiple back-and-forth transmissions between two nodes | RPC, SCP, NFS, PAP, | |
| 4. Transport | Segment (TCP) / Datagram (UDP) | Reliable transmission of data segments between points on a network, including segmentation, acknowledgement and multiplexing | NBF, TCP, UDP | |
| Network / Internet |
3. Network | Packet | Structuring and managing a multi-node network, including addressing, routing and traffic control | AppleTalk, ICMP, IPsec, IPv4, IPv6 |
| Link layer |
2. Data link | Frame | Reliable transmission of data frames between two nodes connected by a physical layer | IEEE 802.2, L2TP, LLDP, MAC, PPP, ATM, MPLS |
| 1. Physical | Bit | Transmission and reception of raw bit streams over a physical medium | DOCSIS, DSL, Ethernet physical layer, ISDN, USB | |
Cross-layer functions:
- ARP is used to translate IPv4 addresses (OSI layer 3) into Ethernet MAC addresses (OSI layer 2).
- Domain Name Service is an Application Layer service which is used to look up the IP address of a given domain name. Once a reply is received from the DNS server, it is then possible to form a Layer 3 connection to the third-party host.
- etc
Owners, Developers, Dangers, Mitigations, Alternatives
| Layer | Example | Practically | Owner | Developed by | Vulnerabilities/Dangers | Securing | Alternatives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | HW - end user equipment | Computer, tablet, phone... | User | Commercial companies: Apple, Siemens, Samsung... | Un-ethical manufacturing, security backdoors, pollution caused by e-waste disposal, | Hard: | Open HW movement; fair-phone; DIY, Repair Cafes, fair-trade... |